Request Information
How does a virology impedance assay work?
In an impedance assay, cells are cultured over an electrode embedded in the surface of the culture dish. Small electrical signals are delivered through the electrode and the presence of cells over the electrode blocks, or impedes, the signal. As host cells are infected, the impedance decreases, allowing real-time assessment of viral infection. Impedance is sensitive to subtle changes in cell morphology, cell-cell interactions, barrier function, attachment, and viability, revealing cytopathic effects prior to cell lysis. For an example of using nonadherent host cells, see our protocol.
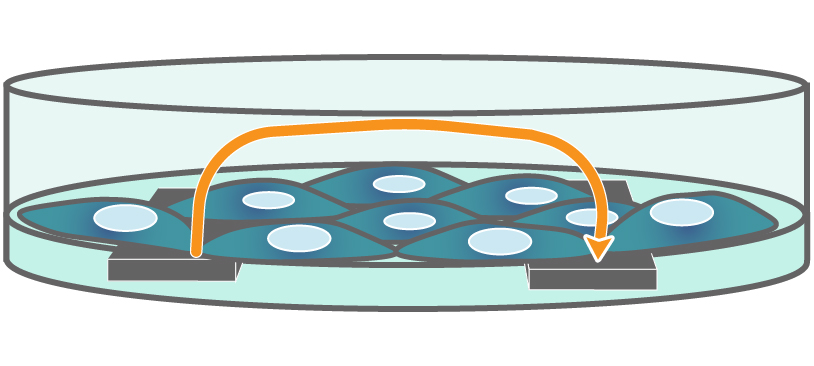
Interdigitated electrodes embedded in the cell culture substrate at the bottom of each well detect small changes in the impedance of current flow caused by cell presence, attachment, and behavior.
What you are missing: Capture the entire infection time course
An infection is a dynamic process and difficult to capture with a single time point. The Maestro Z continuously measures the culture, showing the moment cell health begins to deteriorate, the end result, and everything in between.
As an example, the data below demonstrates a viral titer on the Maestro Z. Unlike common endpoint methods, like plaque assays or endpoint dilutions, the viral titer on the Maestro Z reveals the kinetics of in vitro viral infections for a better understanding of CPEs without the time- and cost-intensive process of repeating multiple endpoint assays.
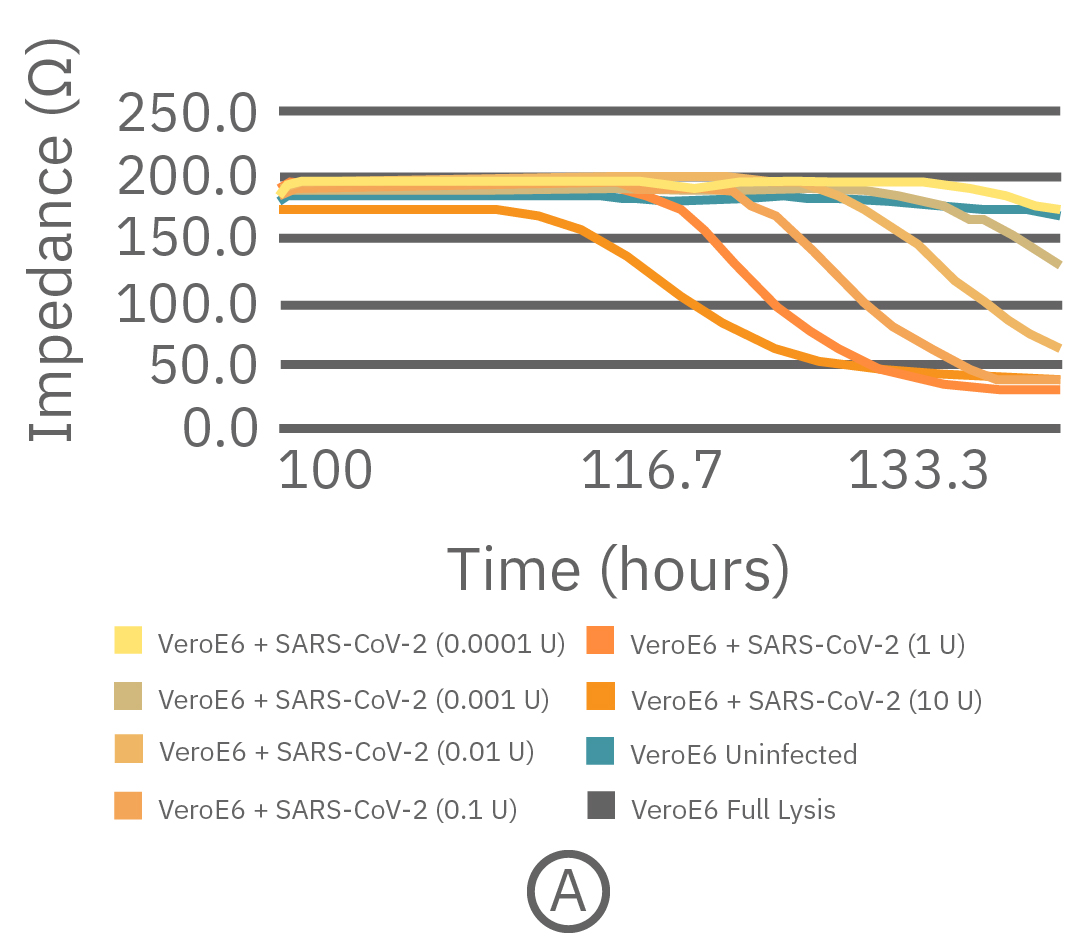
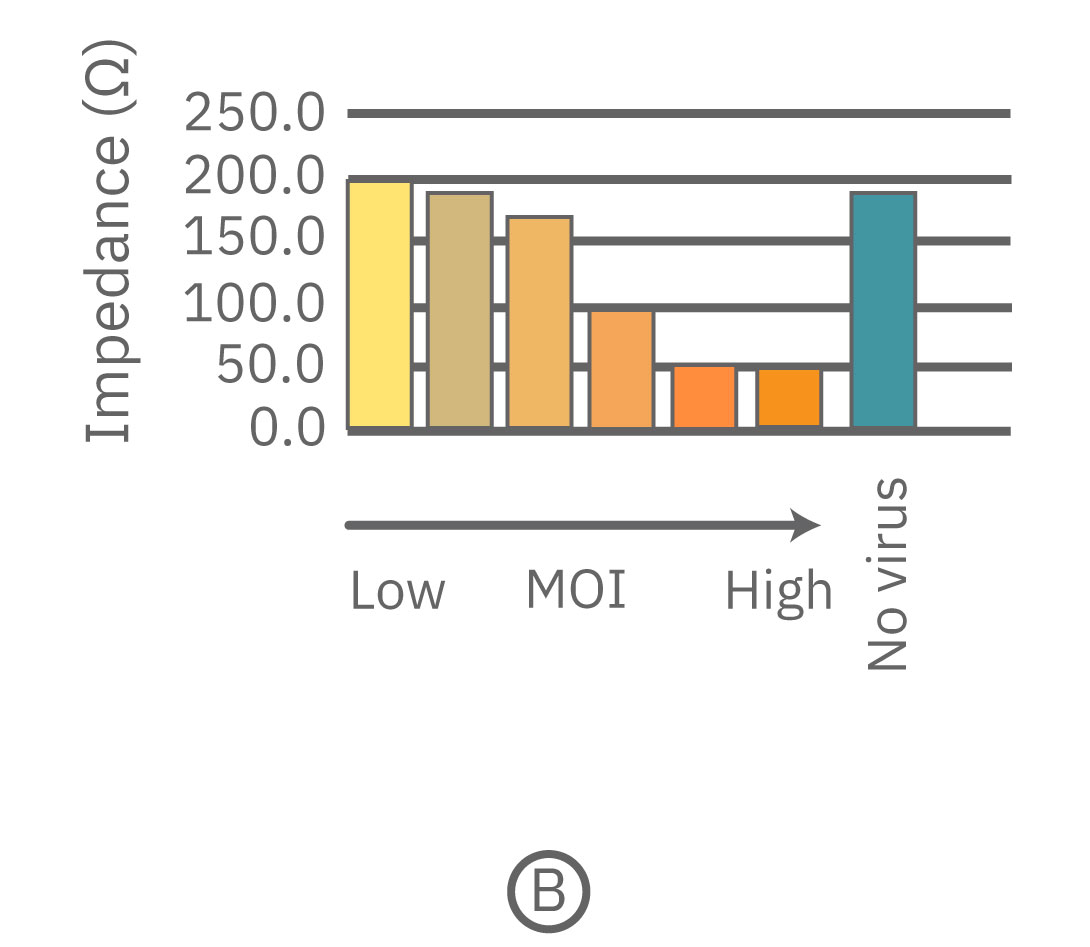
Vero E6 cells were seeded into the CytoView-Z 96-well plate and impedance was continuously monitored on the Maestro Z system. After 96 hours, different concentrations of SARS-CoV-2 virus were added to determine the lowest multiplicity of infection (MOI) that elicits cell death. (A) The full time course of cell death in response to varying amounts of SARS-CoV-2. (B) Bar graph of impedance at 130 hours
The same principle holds when comparing the virulence of multiple strains or the resistance of modified host cells. How sudden the onset and severity of the response can all be quantified in a single 96-well plate. The benchtop system is self-contained, environmentally controlled, with automated data acquisition.
Finding a cure
The Maestro Z can be used to assess the effectiveness of neutralizing antibodies, antivirals, and vaccines. Viruses evolve rapidly, continuously presenting new targets and making older treatments less effective. The Maestro Z is designed to provide the speed and ease to keep up.
With the recent outbreaks of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), Ebola, Zika, influenza, and other viral infections, efforts to develop broad-spectrum antivirals, which are effective against a wide range of viral infections, have increased to treat emerging and re-emerging viruses. Development is challenging as compounds must selectively inhibit viral replication without damaging the host.
A comparison of antiviral candidates can demonstrate their respective effectiveness and dosing range. In the data below, four compounds were tested against SARS-CoV-2 grown on Vero E6 cells.
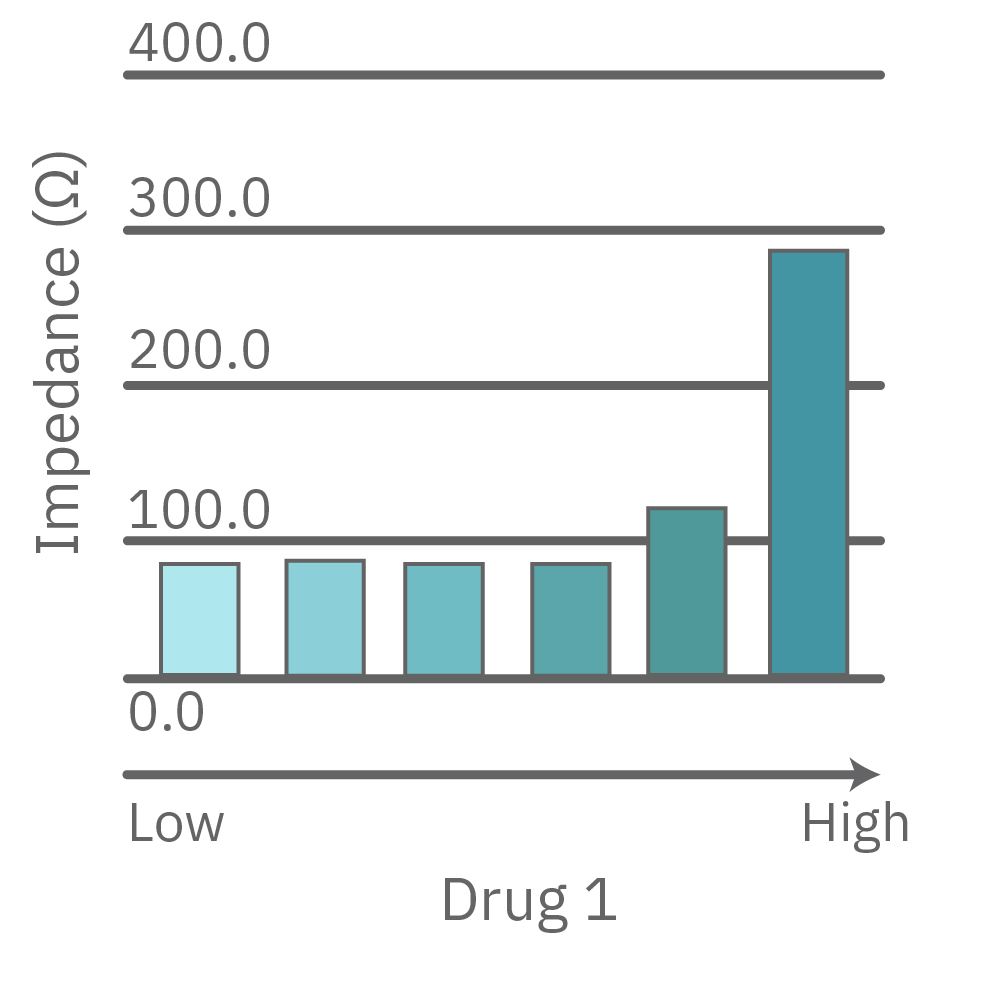
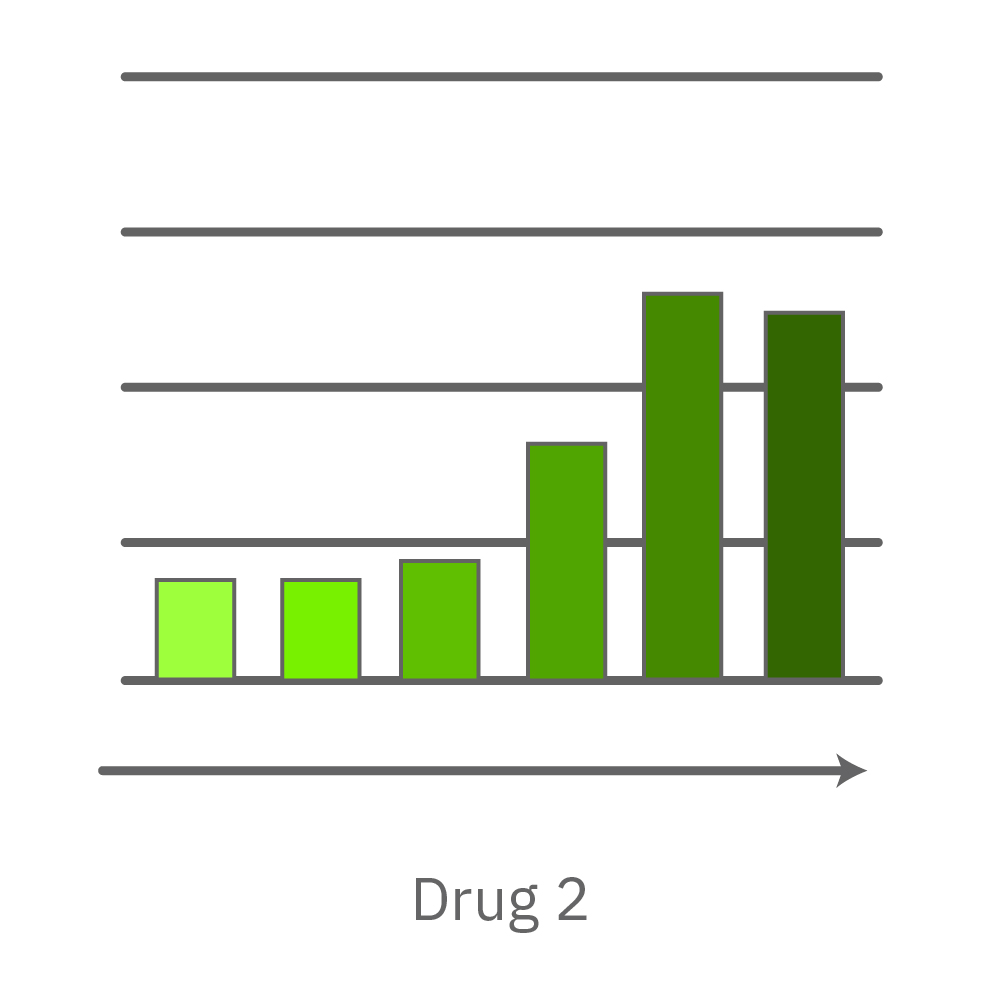
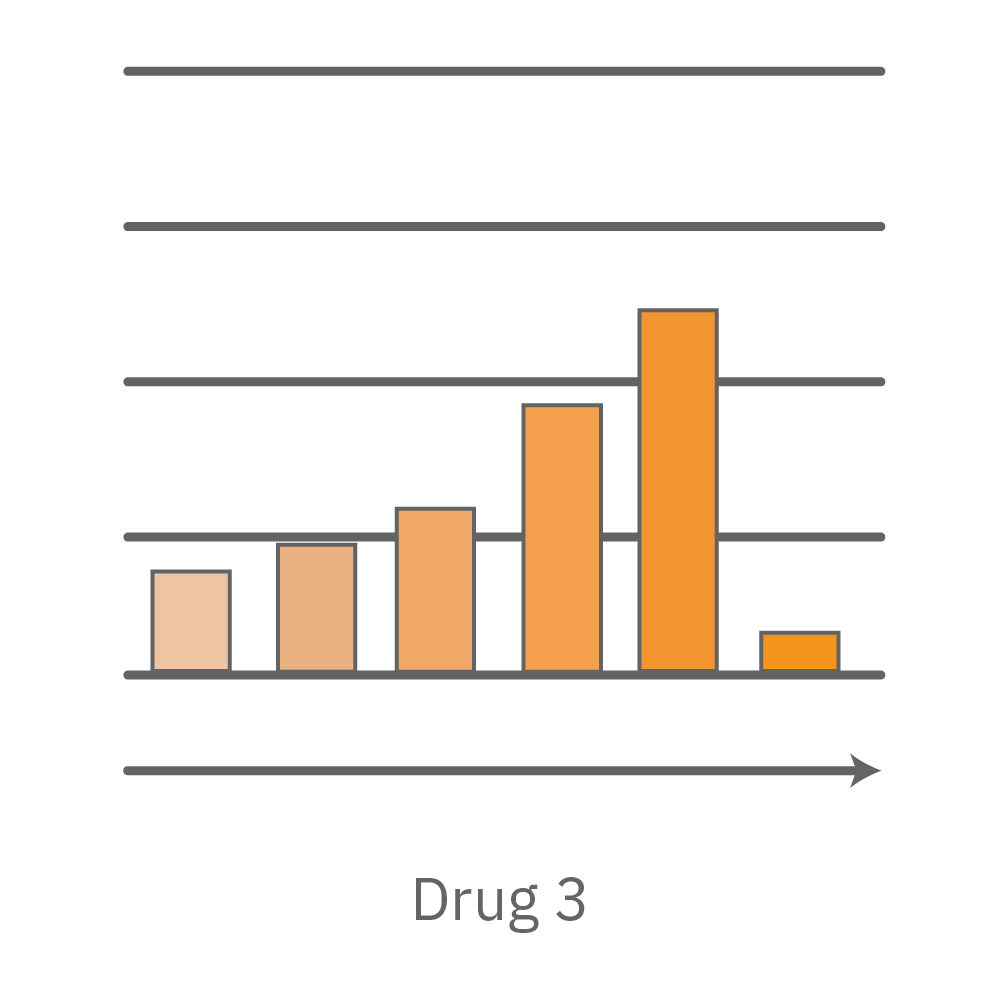
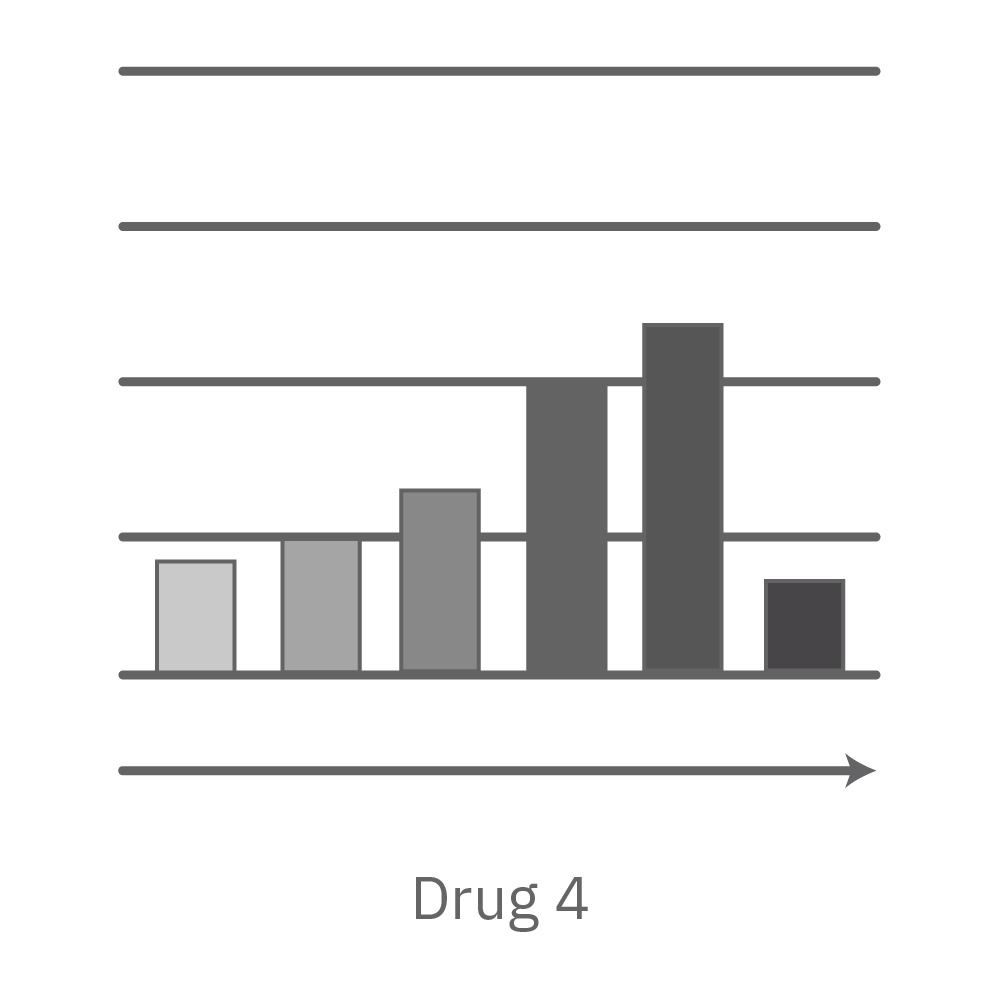
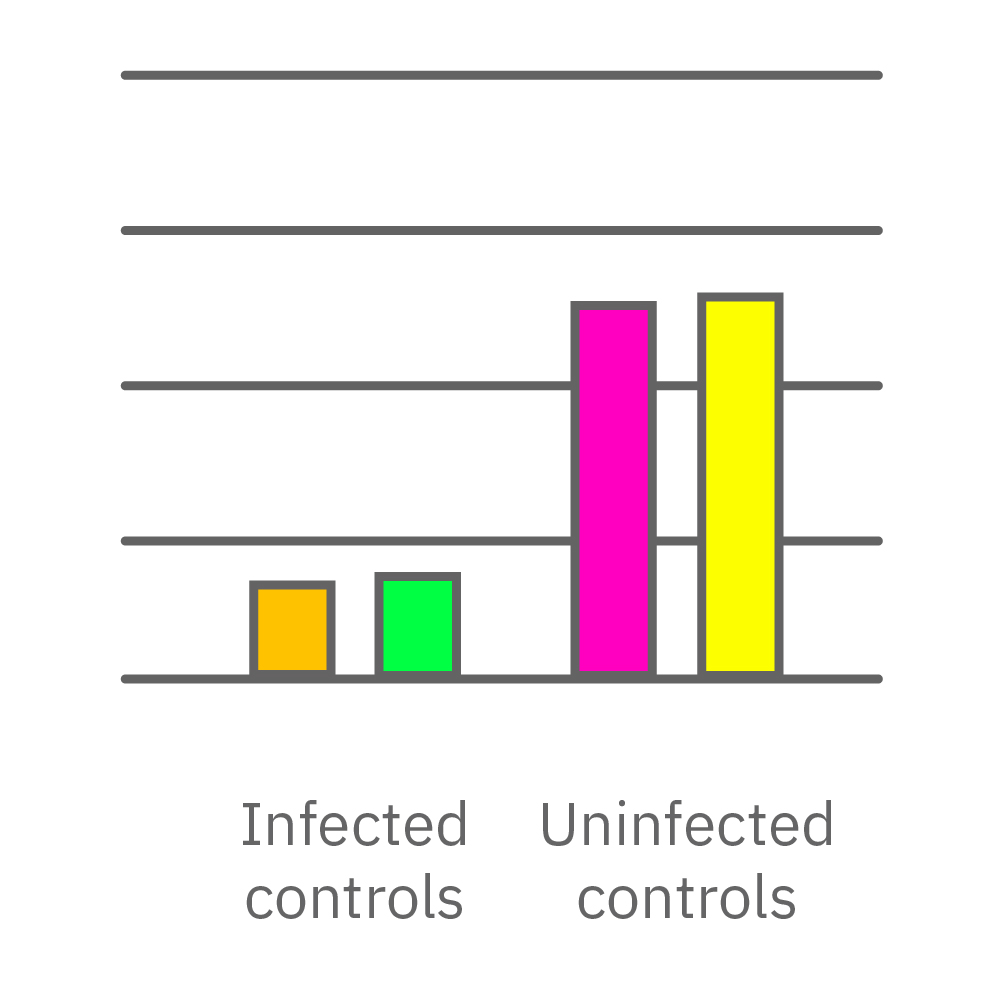
Vero E6 cells were seeded into the CytoView-Z 96-plate and impedance was continuously monitored on the Maestro Z system. After 24 hours, test compounds and SARS-CoV-2 were added. Antiviral drugs resulted in a dose dependent decrease in cell death in the presence of virus with the exception of Drugs 3 and 4 at their highest concentrations, likely due to their own toxicity. Infected and uninfected wells show low and high impedance values, respectively.
In much the same way neutralizing antibodies or vaccines may be tested. Antibodies are either directly added to the culture or, as the case with vaccines, serum from vaccine recipients is inoculated with virus and cultured on host cells.
Get more from your virology assays
Since the Maestro Z monitors continuously, you can evaluate if a therapeutic approach halts an infection or merely slows it down. Effectiveness and safety of therapeutic candidates can be evaluated concurrently. Accurate detection and rapid quantification of cytopathic effects with Maestro Z can strongly augment, be multiplexed with, or even replace many traditional virology assays and makes a great tool for any lab.
To see how Maestro Z was used to identify potential targets for SARS-CoV-2 by the Basler lab (University of Georgia).
