脳内には複雑な回路網が多数存在し、独自に或いは相互に連携しながら機能しています。更に、神経システム内の回路網は、他の様々な生物学システムと相互に作用しながら、人体の生命活動を機能させています。中央分離形状のインサートを使用した in vitro モデルにより、2つの神経回路網、或いは細胞集団の機能的結合や相互作用を検証することが可能です。
Axion BioSystems の Maestro Pro、Edge システムでは、インサートを用いて同一 well 内に複数の神経培養を作成し、培養間の機能的ネットワークの形成を追うことができます。神経回路網 (培養) 間の機能的結合や、シナプス伝達の遮断効果の検証に有用です。
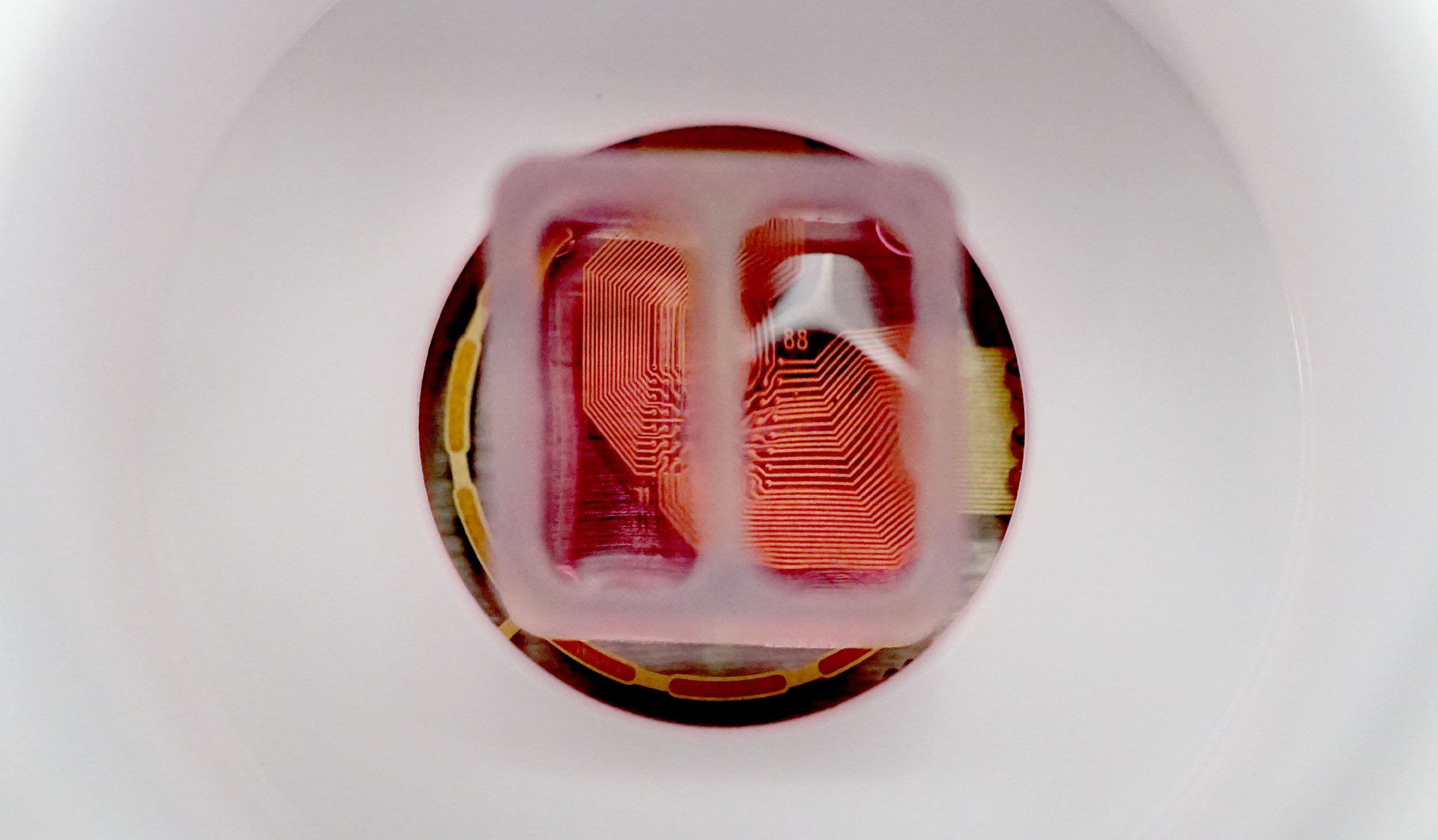
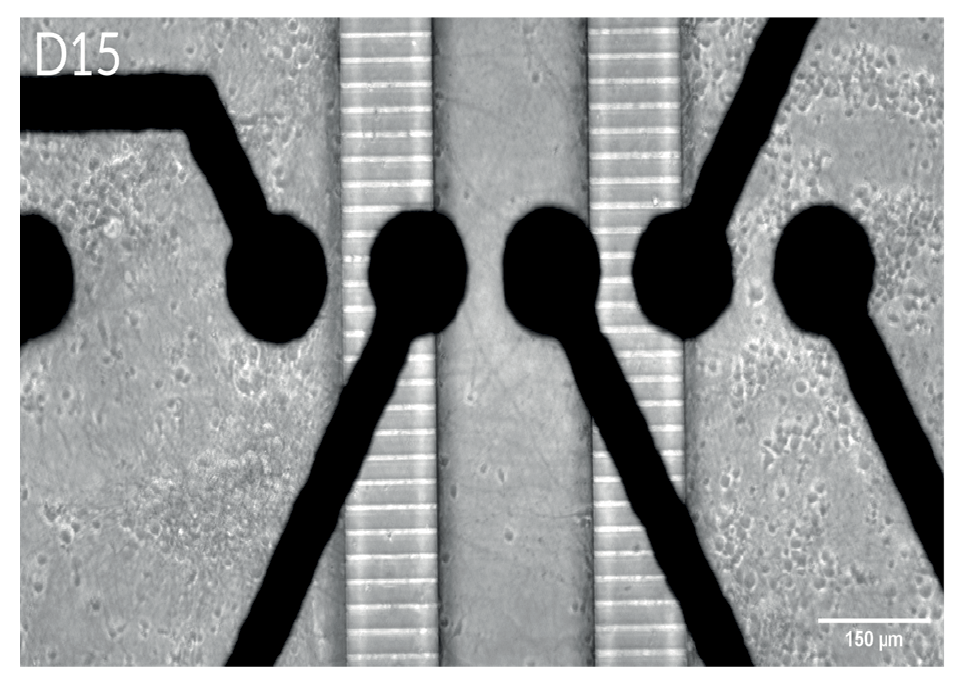
中央分離形状のシリコン製インサート (ibidi, カタログ番号 80209) を CytoView MEA 6-well プレート (M384-tMEA-6W) の well 内に設置し、2つの皮質神経細胞培養を作成しました。培養開始から7日後にインサートを除去し、更に継続して神経細胞を培養しました。インサート除去から3日後、2培養の分離部分(細胞非播種)に神経突起の伸長が見られました。インサート除去から10日後には、2つの神経回路網(培養)から同期した電気的な応答が得られ、機能的な結合が示唆されました。
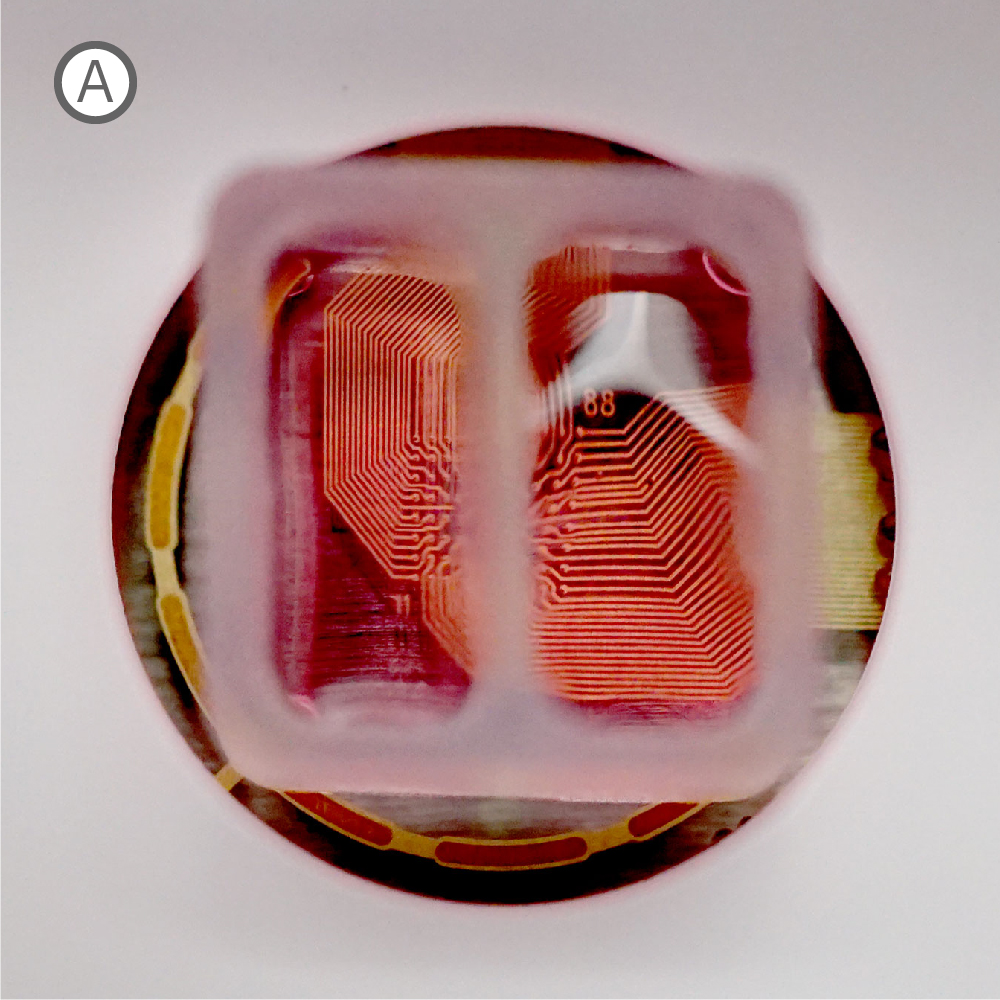

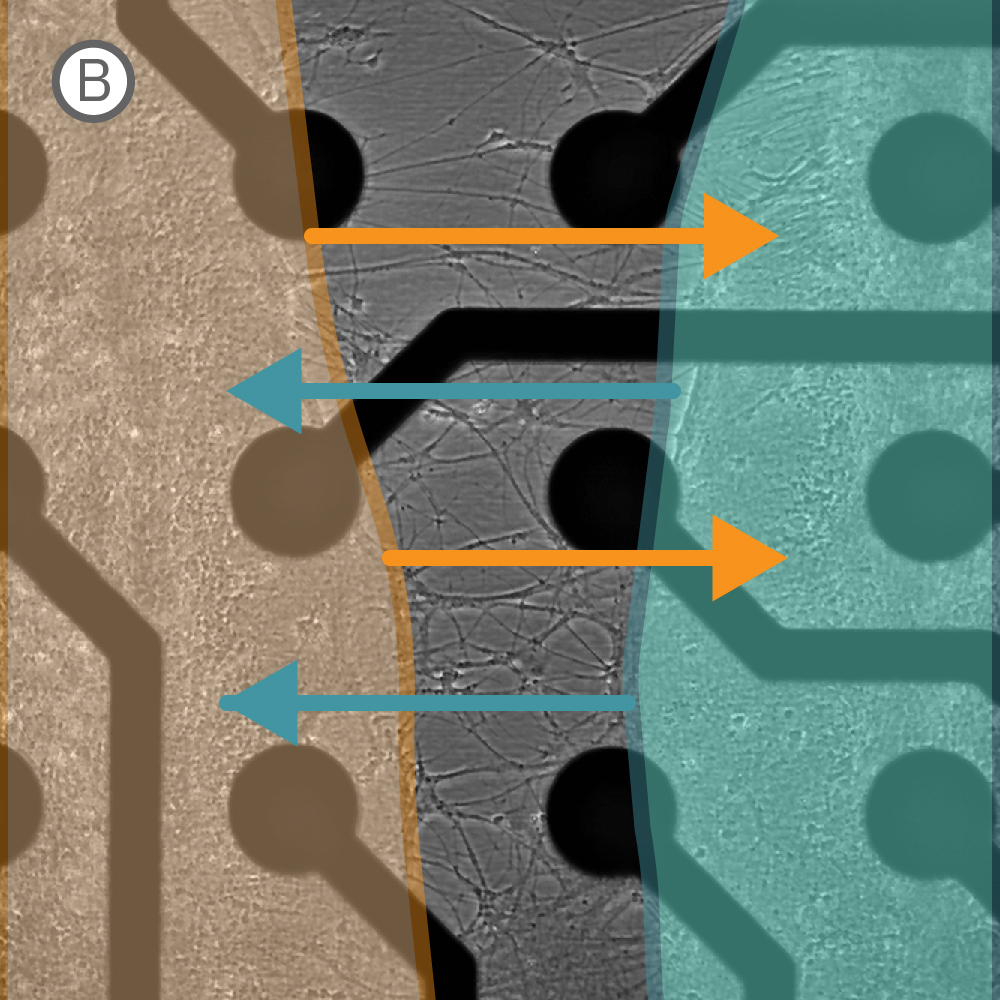
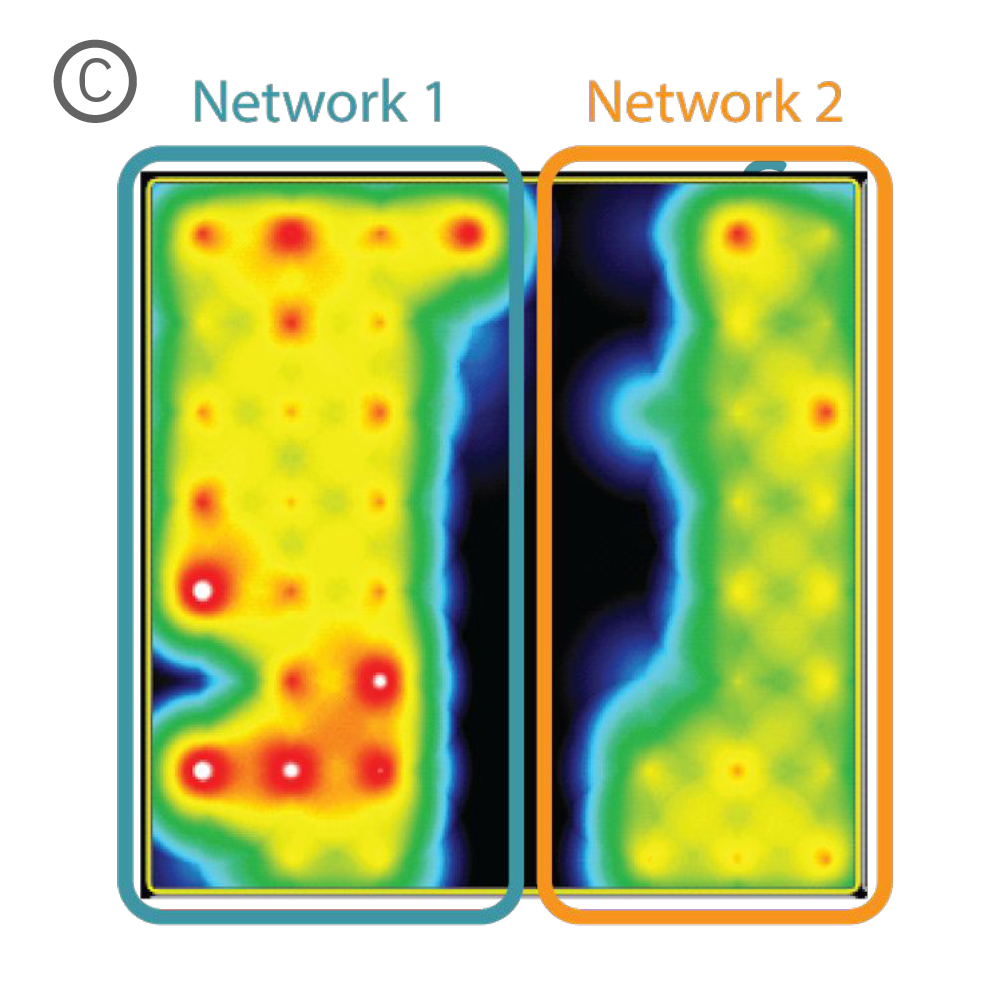

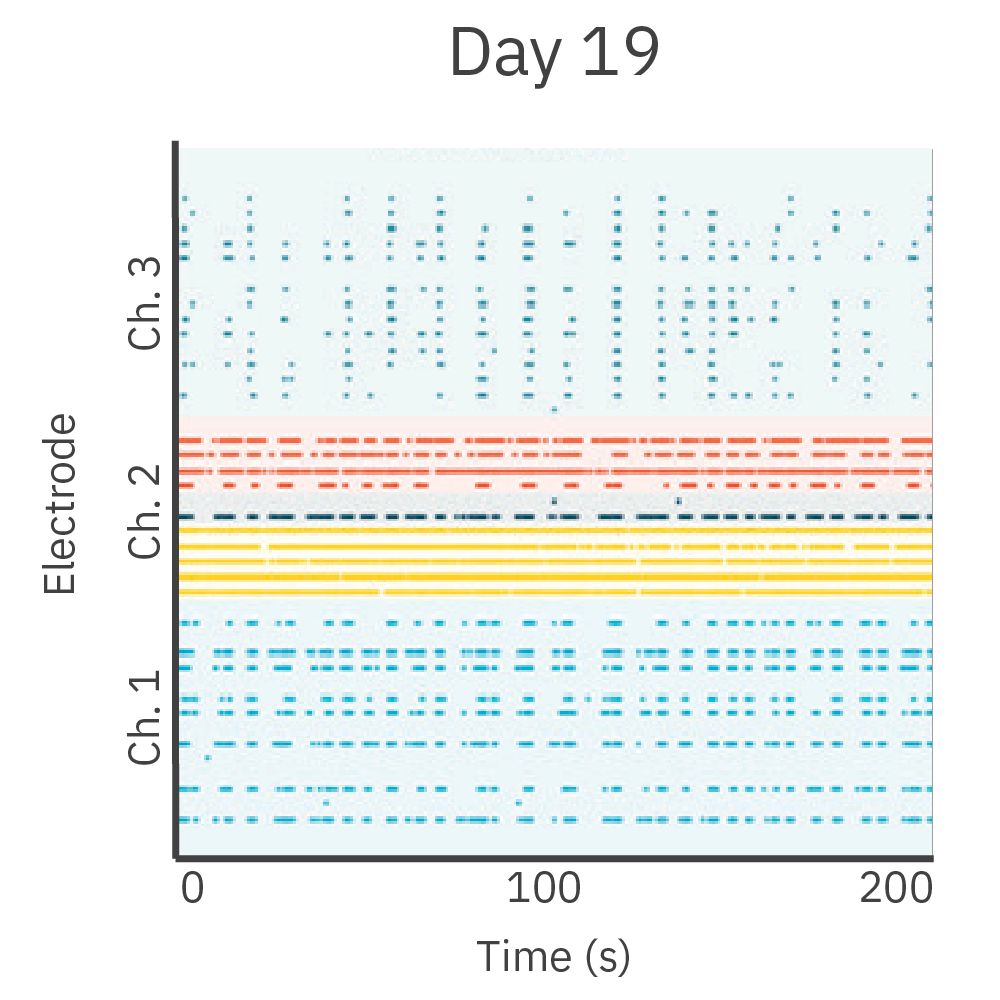
A) Well 内に設置されたシリコン製インサート。 各コンパートメントにそれぞれ細胞を播種・培養し、48時時間後にインサートを除去した。B) インサート除去から10日後のwell内の様子。細胞非播種部分への、神経突起の伸長が見られた。C) 特定 well から得られたActivity map。各 Network (培養) の活動に同期が見られた。D) 培養開始から17日後に得られたスパイクラスタープロット。Network 1 (培養1)、Network 2 (培養2)がそれぞれ独立してバースティングした後、Network 1からNetwork 2とバースティングが続くwell内のイベントが見られた。
目的: 異なる神経サブタイプ間におけるシナプス結合の探索。ブレインオンチップ (Brain-on-a-chip)モデルにより、脳の異なる領域の相互作用を見ることが可能です。
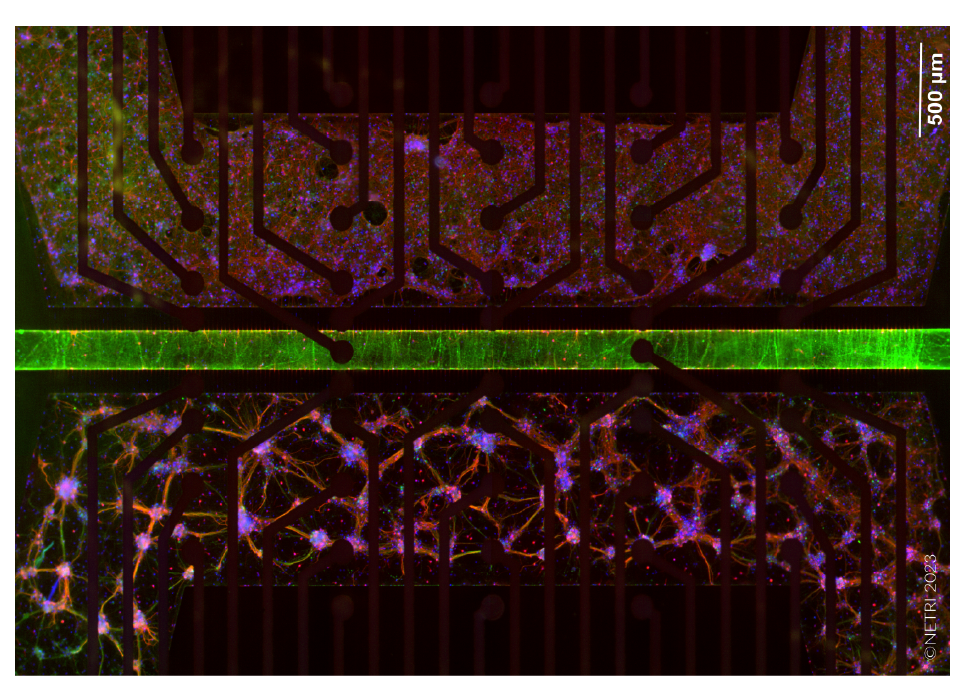
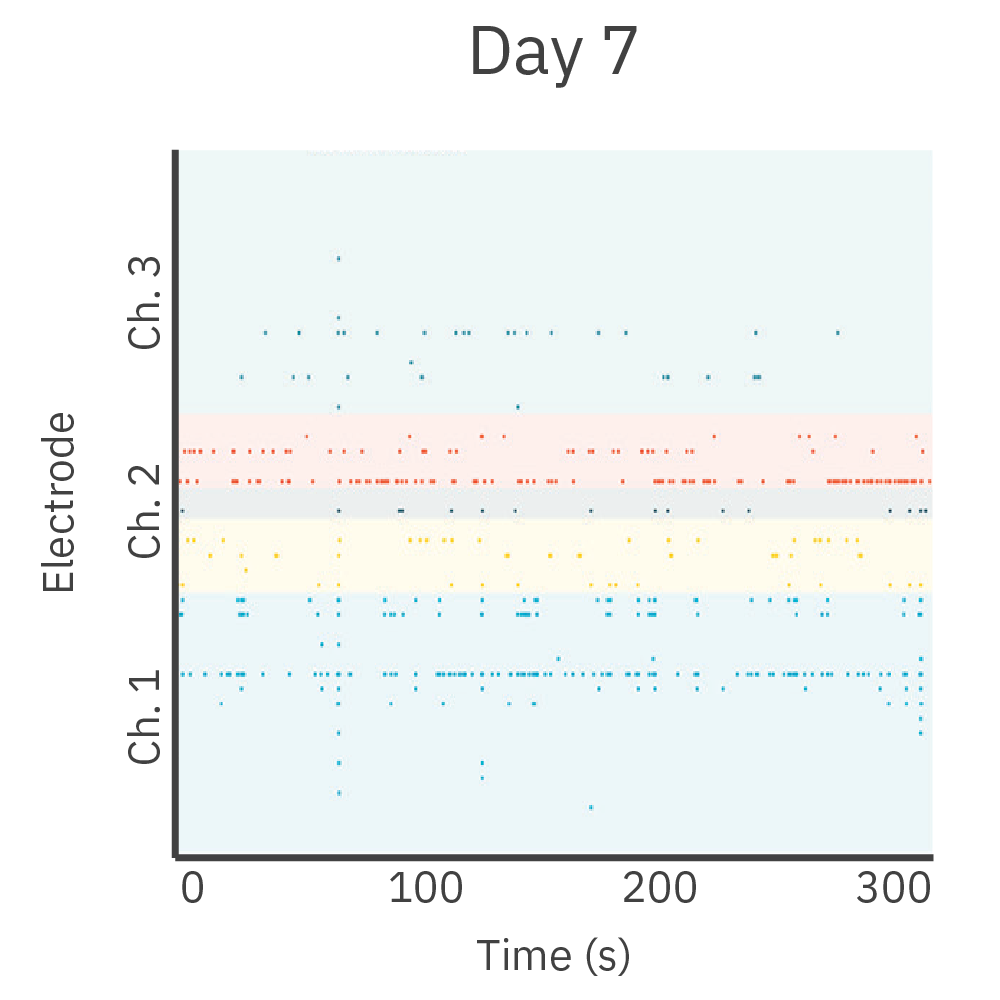
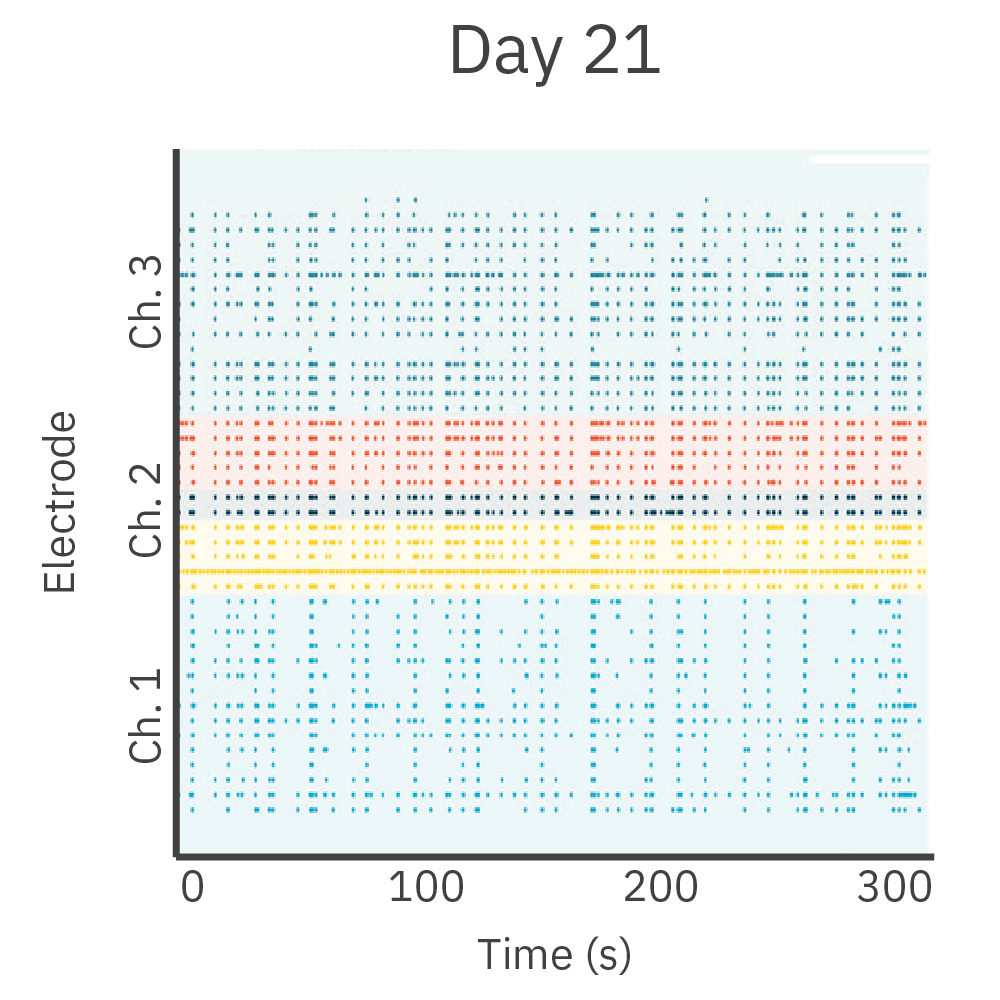
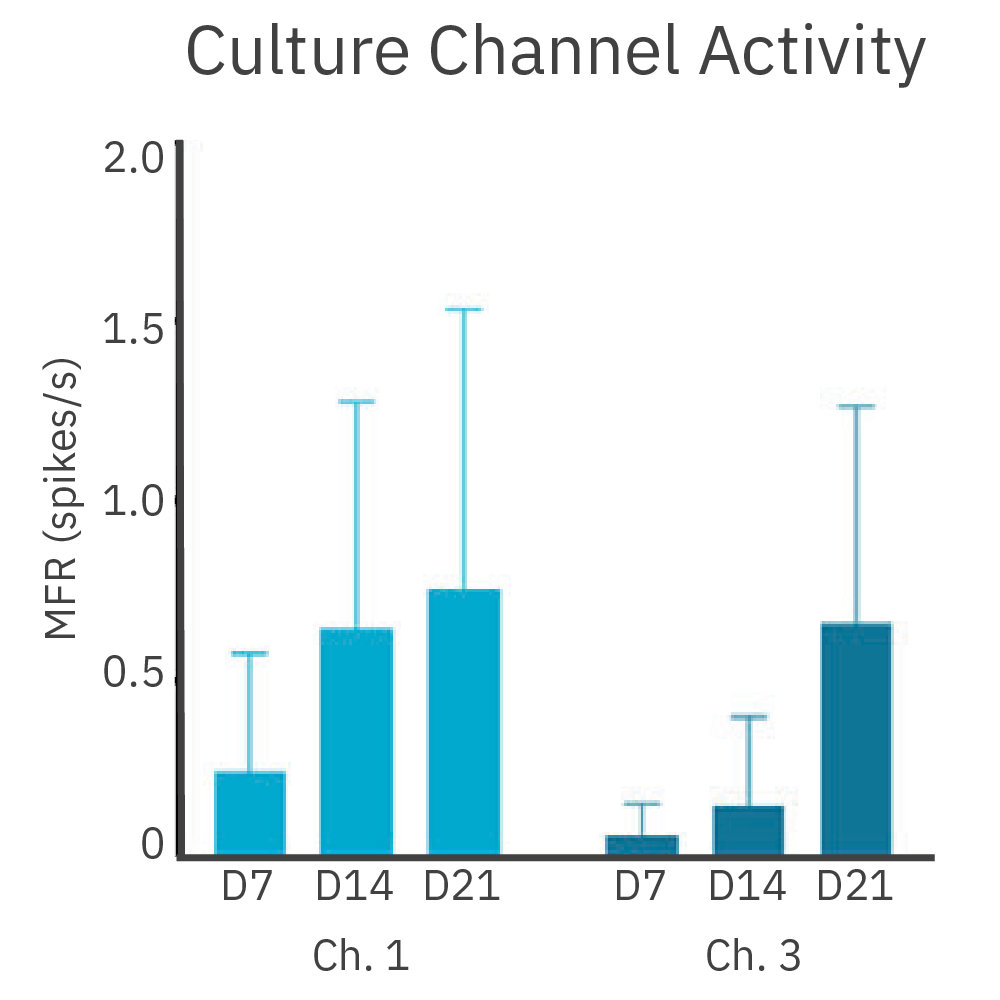
皮質、海馬の両神経細胞をDuaLink MEA (Netri社) の分離されたチャンバー内に培養し、 Maestro MEA プラットフォーム で21日間に渡り電気的な活動を測定しました。
結果: 新たなシナプスの形成に伴い、チャンバー間の同期発火が増加しました。
目的: 神経突起の成長と活動の追跡。神経細胞の成熟や投射機能の理解は、神経再生医療の開発を加速させます。
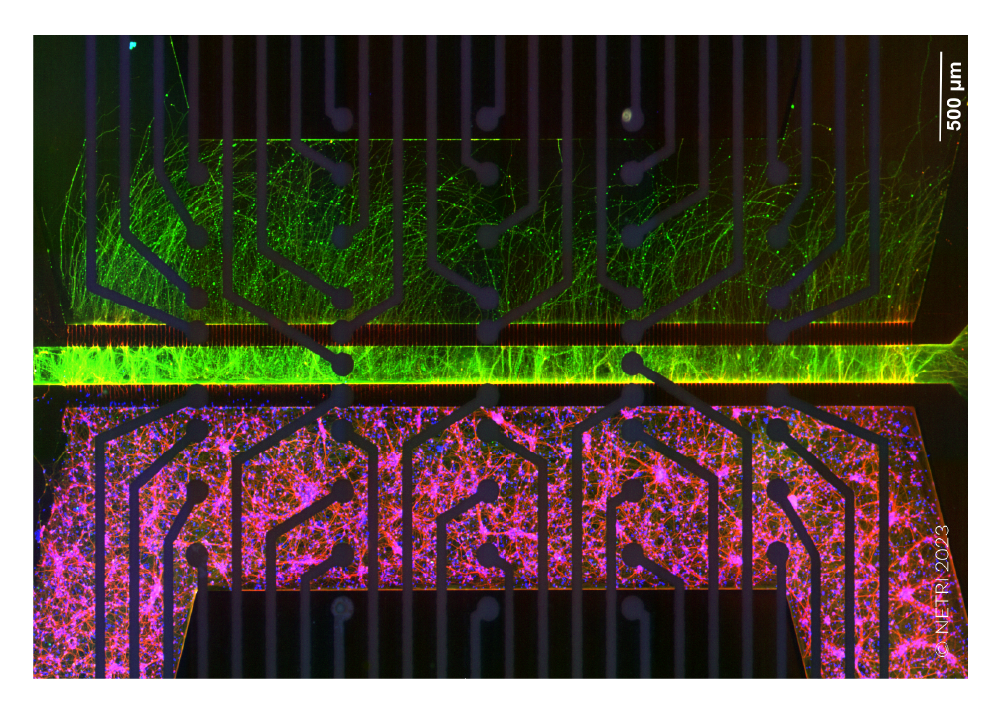
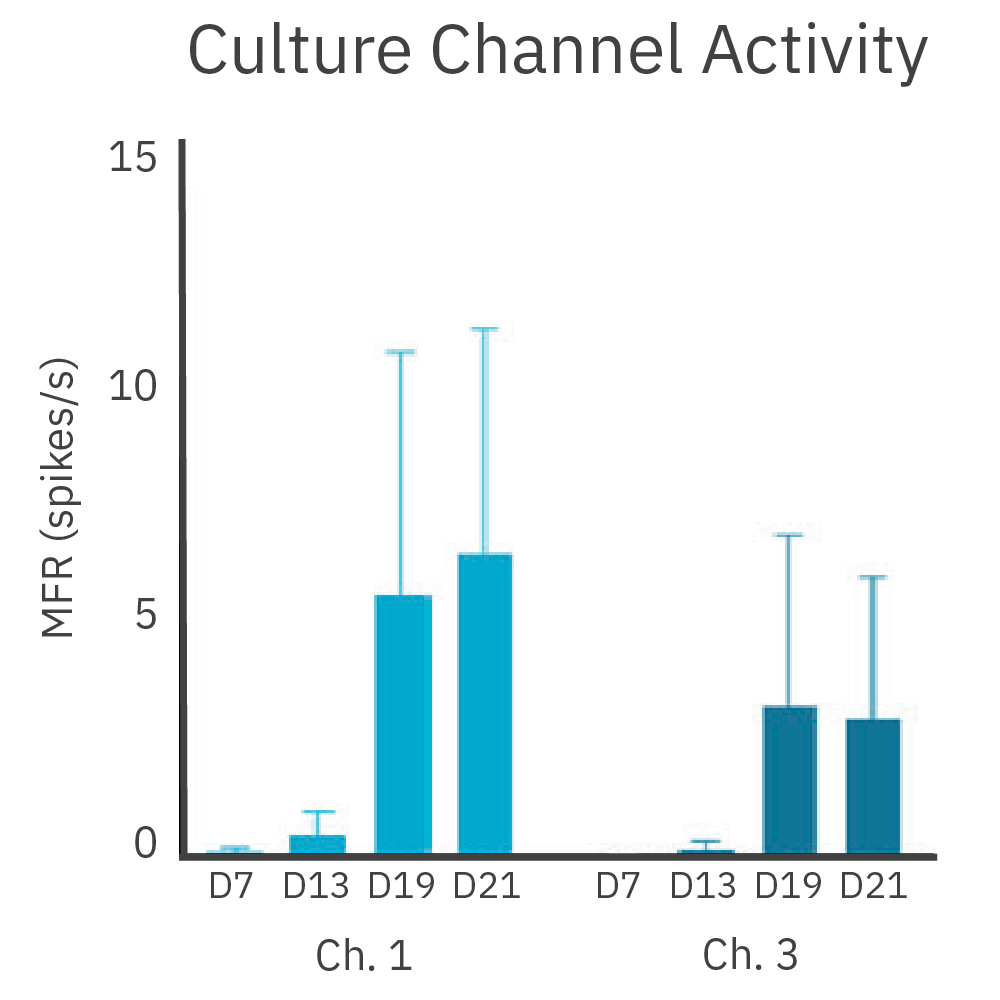
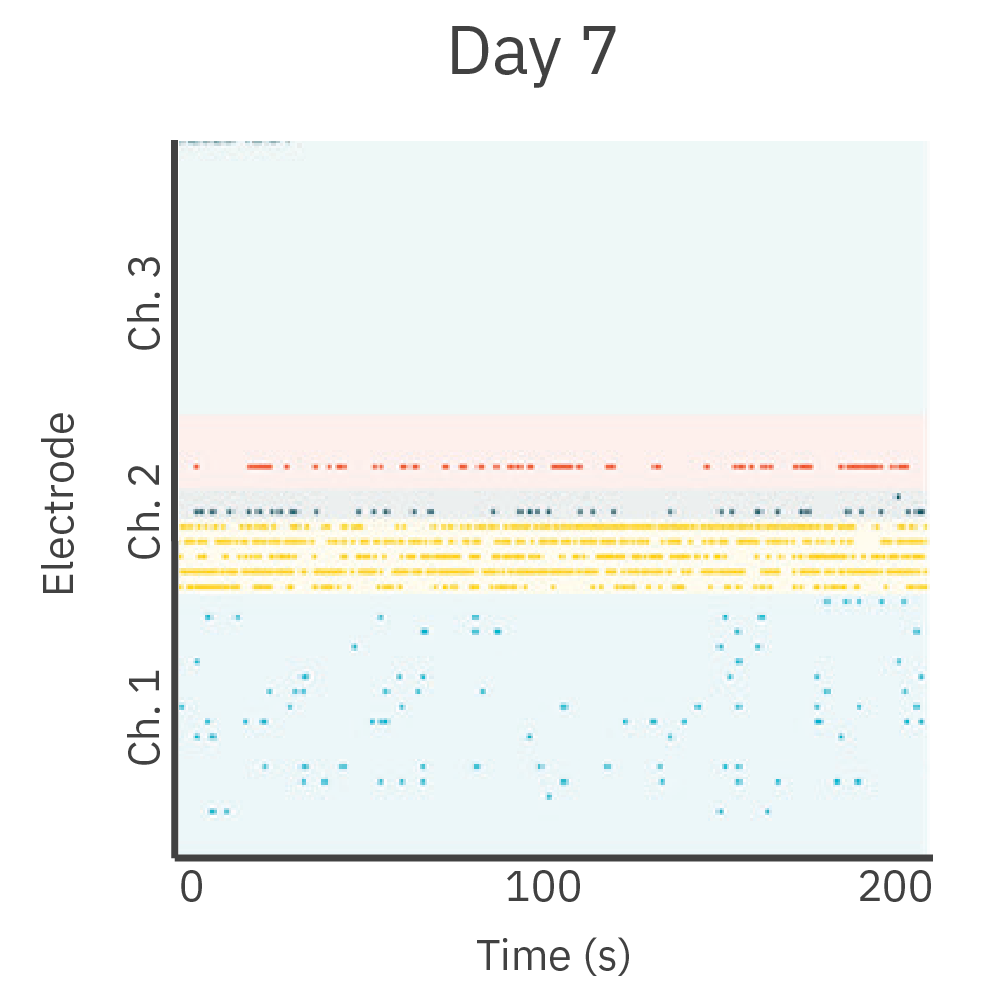
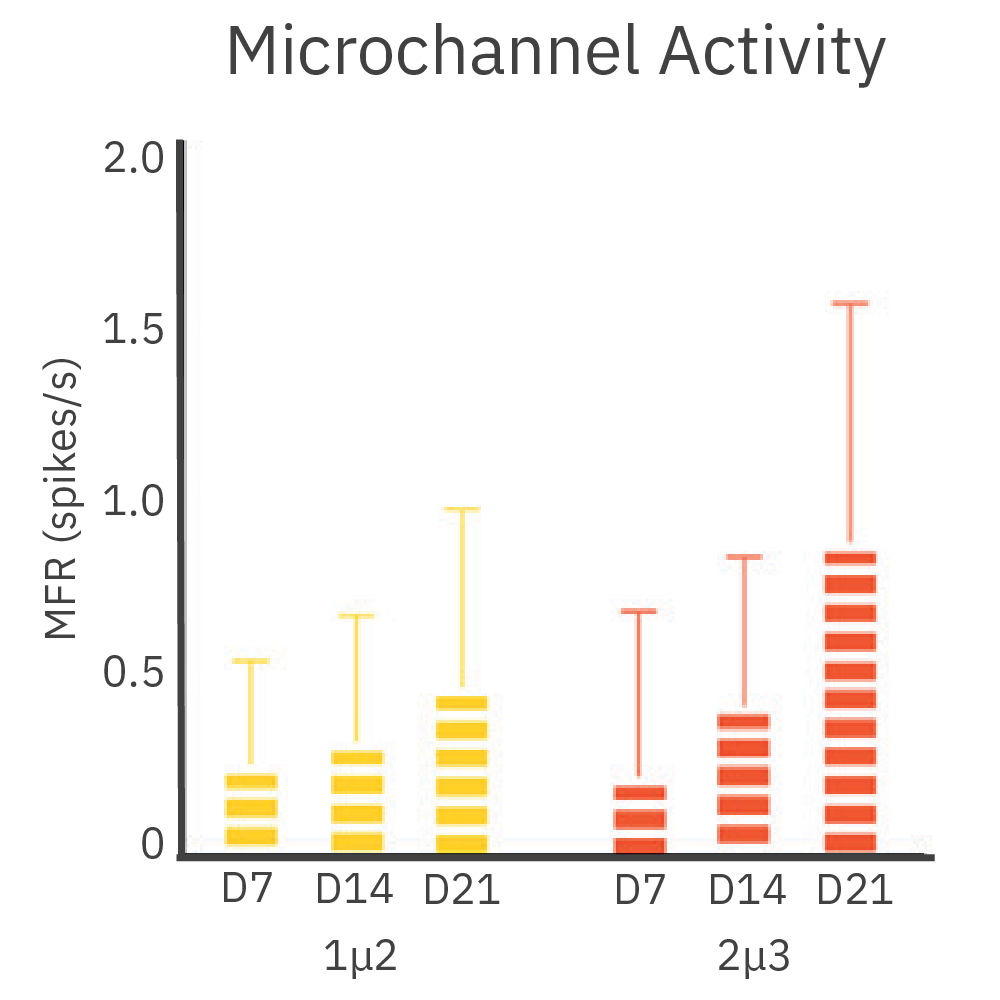
皮質神経細胞を、DuaLink MEA (Netri社) の1チャンバー内に培養し、Maestro MEA プラットフォームで電気的な活動を測定しました。
結果: 新しい神経突起がプレート内の空チャンバーをに伸長し、それに伴い電気的な活動が増加しました。また、この活動は、皮質細胞(別チャンバー内)の活動と同期しました。
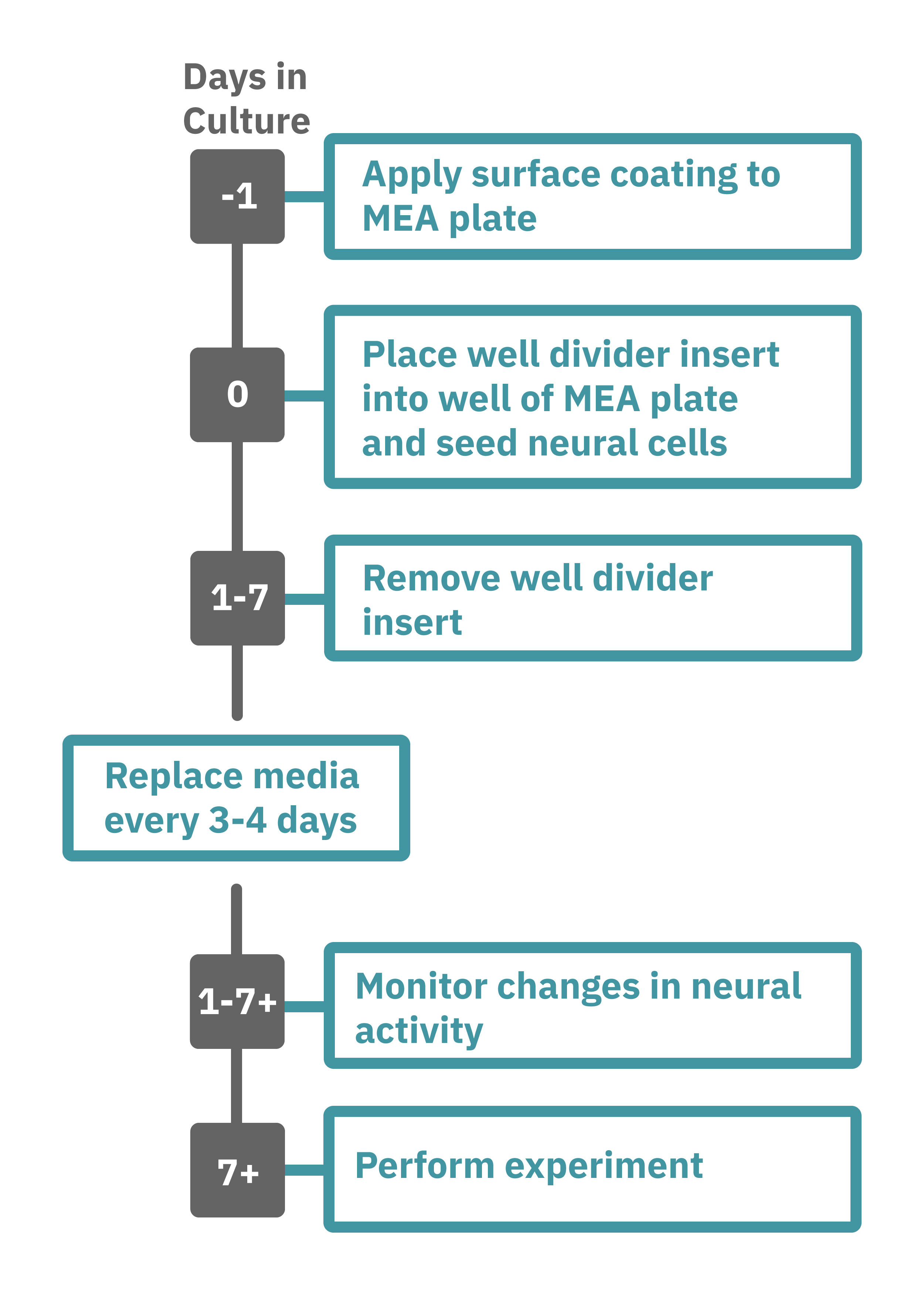
Maestro Pro、Edge によるアッセイは非常に簡単です。CytoView MEA 6 wellプレート (M384-tMEA-6W) の各 well 内に、中央分離形状のインサート (ibidi, カタログ番号 802029) を設置します。各コンパートメントに細胞を播種し培養を開始します (Day 0)。
細胞が MEA プレート底面に接着していることを確認した後 、インサートを除去します(1~7日後)。装置に搭載された温度・CO₂ 濃度コントローラを作動させ、MEAプレートを搭載し、ラベルフリーで測定を行います。測定後は、AxIS Navigator の神経モジュールソフトウエア で解析します (Day 2+)。



